Kafka Mapper
The following application was created by a project with
The goal was to implement an application that is capable of transforming incoming MQTT topics to a format that is compliant with Kafka, as the original data was streamed with MQTT, whereas the subscriber was only able to receive data sent in Kafka JSON format.
Basic information about the application and key features
The MQTT-to-Kafka mapper is based on a spring boot java microservice architecture. Therefore, one of the key features of the application is the low consumption of resources, as the framework allows for the efficient distribution and usage of resources in general.
Another key feature provided by this application is the mapping by objects. This feature allows the application to transmit the topic from its very origin (MQTT) up to its destination (Kafka).
The next feature is the automatic detection of optional values inside the input stream. This particularity allows the application to determine these values and redirects it to the output stream. It is also possible to set a default flag for the output elements in the config file.
It is also possible to pass MQTT Topics to the same Kafka Topics.
Lastly, the application also supports simultaneous, the conversion of multiple and single MQTT Topics to Kafka Topics at once.
Architecture and functional principles of the MQTT-to-Kafka mapper
Preconditons
Before starting the application, you must ensure that both the MQTT server and the corresponding Kafka server are running.
The current version does not have an interface that performs checks such as the above-mentioned prerequisites, as in a general operation both servers must be active.
In case these preconditions are not met, the application will throw multiple errors and will eventually crash.
Functional principles
At first, a JSON string is being sent via MQTT (HTTP is possible as well). This string is being directed into the MQTT-to-Kafka mapper, where the string is then being transformed into a Kafka-compliant format, which is predefined.
The application then executes the mapping by objects. For this process, a configuration file had been created which defines all rules necessary for the execution of this mapping. As soon as the mapping is done, the string is transmitted to the Kafka broker and can then be used for further business processes.
Version Informations
The application is currently stable and the actual status is stable (Version 1.0.1).
| Version | Status | Change Description |
| 0.9.1 | Beta | |
| 1.0.1 | Stable |
Installation
Configuration File
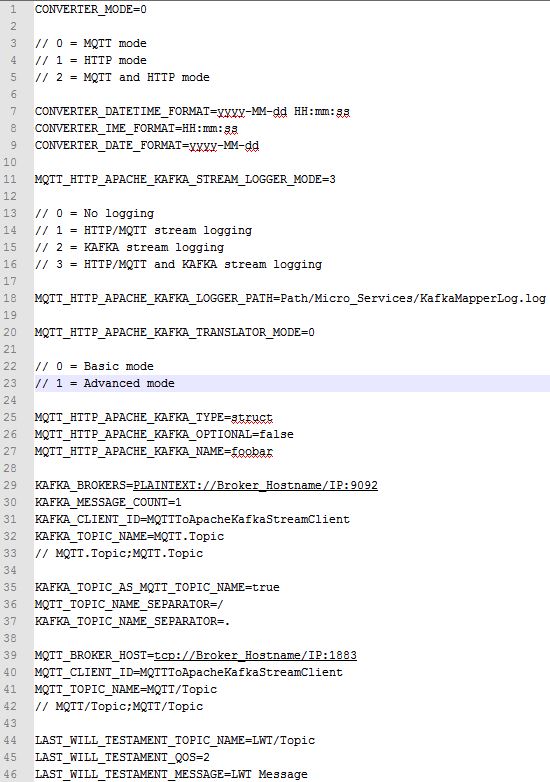
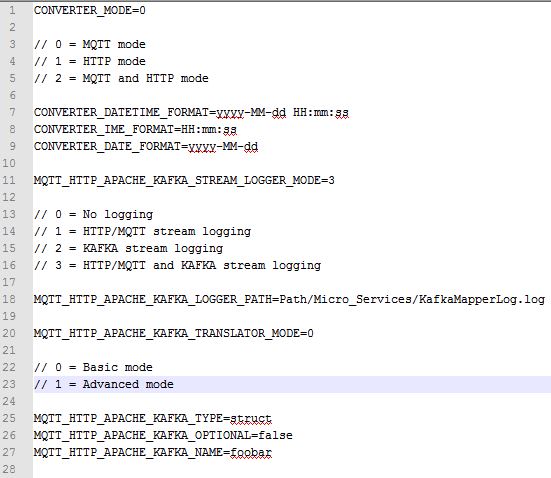
The following table explains you, the individual functions of the configuration file.
| File Option | Example | Meaning |
| General Config | ||
| CONVERTER_MODE | 0 | MQTT mode (Application works only with valid MQTT JSON commands) |
| 1 | HTTP mode [URL: localhost:8080/HTTPToApacheKafkaConverterApi?jsonMessage:{}] (Application works only with valid HTTP JSON commands) | |
| 2 | MQTT and HTTP mode [URL: localhost:8080/HTTPToApacheKafkaConverterApi?jsonMessage:{}] (Application works with valid HTTP JSON and MQTT JSON commands) | |
| CONVERTER_DATETIME_FORMAT | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss | Define the incoming DateTime format |
| CONVERTER_TIME_FORMAT | HH:mm:ss | Define the incoming Time format |
| CONVERTER_DATE_FORMAT | yyyy-MM-dd | Define the incoming Time format |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_STREAM_LOGGER_MODE | 0 | No logging (No logging of the input and output stream) |
| 1 | HTTP/MQTT stream logging (O | |
| 2 | Kafka stream logging (O | |
| 3 | HTTP/MQTT and Kafka stream logging (Logging of the input and output stream) | |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_LOGGER_PATH | Path/Micro_Services/MqttAndHttpApacheKafkaConverterLog.log | Define the log path and file |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_TRANSLATOR_MODE | 0 | Basic mode (Translation of the input to the output stream) [Example: {“name”:”value”}] |
| 1 | Advanced mode (Translation and conversion of the input to the output stream) [Example: {“payload”:{“name”:”value”}, “name”:”foobar”,”optional”: false,”type”:”struct”,”fields” :[{“field”:”name”,” optional”:false,”type”:”string” }]}] | |
| Apache Kafka Config | ||
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_TYPE | struct | Define the Kafka output stream type |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_OPTIONAL | false | Don’t use the optional flag for all elements of the Kafka output stream (Information: By default, the application checks the input stream and determined the optional values. You can set here the flag inside the output stream, to not using these values) |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_OPTIONAL | true | Use the optional flag for all elements of the Kafka output stream (Information: By |
| MQTT_HTTP_APACHE_KAFKA_NAME | foobar | Define a name for the output stream |
| KAFKA_BROKERS | PLAINTEXT:// Kafka_Broker_Hostname:Kafka_Broker_Port | Define the Kafka Broker Hostname or IP and the Port (Default: 9092) |
| KAFKA_MESSAGE_COUNT | 1 | Define the Kafka message count |
| KAFKA_CLIENT_ID | MQTTToApacheKafkaStreamClient | Define the Kafka client ID |
| KAFKA_TOPIC_NAME | MQTT.Topic | Define the Kafka T |
| MQTT.Topic;MQTT.Topic | Define the Kafka T | |
| KAFKA_TOPIC_AS_MQTT_TOPIC_NAME | true | Enable forwarding the MQTT Topic to the Kafka T |
| false | Disable forwarding the MQTT Topic to the Kafka T | |
| MQTT_TOPIC_NAME_SEPARATOR | / | Define the MQTT T |
| KAFKA_TOPIC_NAME_SEPARATOR | . | Define the Kafka T |
| MQTT/ HTTP Config | ||
| MQTT_BROKER_HOST | tcp://MQTT_Broker_Hostname:MQTT_Broker_Port | Define the MQTT Broker Hostname or IP and the Port (Default: 1883) |
| MQTT_CLIENT_ID | MQTTToApacheKafkaStreamClient | Define the MQTT client ID |
| MQTT_TOPIC_NAME | MQTT/Topic | Define the MQTT Topic |
| MQTT/Topic;MQTT/Topic | Define the MQTT T | |
| LAST_WILL_TESTAMENT_TOPIC_NAME | MQTT/Topic | Define the Last Will and Testament T |
| LAST_WILL_TESTAMENT_QOS | 2 | Define the Last Will and Testament QOS |
| LAST_WILL_TESTAMENT_MESSAGE | The device is currently not available. | Define the Last Will and Testament message |
Requirements
- The application was developed for Java 8 and may also run under higher Java versions.
Establishment
- Download the correct file for your Operating System.
- Unpack the file and copy the Jar and configuration folder & file to your local Operating System.
- Adjust your favorite user and set the correct rights at the Jar file (
sudo chown user:user Path/Kafka_Mapper.jar &sudo chmod 755 Path/Kafka_Mapper.jar) - Optional by Linux and MAC OS X Systems: Copy, implement and customize the Service Script.
- Download and copy the Script from here.
- Place the Script inside your /etc/init.d directory.
- Set the correct rights to your Script (
sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/kafka -mapper). - Set the correct owner to your Script (
sudo chown root:root /etc/init.d/kafka -mapper). - Customize the path inside the Script (
sudo nano /etc/init.d/kafka -mapper). - Activate the Script and implement it your system start process with (
sudo systemctl enablekafka -mapper).
- Start the Service Script (
sudo servicekafka -mapper start) to run the application. - Or start the MQTT_Kafka Jar file (/usr/bin/java -jar Path/Kafka_Mapper.jar &) to run the application.
Download
Donations
If you want you can support my work. The corresponding PayPal link will follow shortly.
License Agreement
You can find the license agreement here.
Support
Please, contact me if you find a bug or you need help!